anti theft rfid tag
September 18, 2025
anti theft rfid tag proposal! anti theft rfid tag official support.GOV,anti theft rfid tag active!
<h1>Anti Theft RFID Tag: The Ultimate
nfc huawei gt5 for Modern Security Challenges</h1>

<h2>Introduction to Anti Theft RFID Technology</h2>
In an era where security concerns are escalating across various sectors, the <strong>anti theft rfid tag</strong> has emerged as a revolutionary tool in asset protection and inventory management. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology utilizes electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be read from several meters away, without requiring a direct line of sight. The integration of anti-theft capabilities into RFID systems has significantly enhanced their utility, making them indispensable in retail, logistics, healthcare, and personal asset management. This article delves into the mechanics, applications, benefits, and future trends of <strong>anti theft rfid tag</strong> solutions, providing a comprehensive overview of their role in contemporary security frameworks.


<h2>How Anti Theft RFID Tags Work</h2>

<h3>Basic RFID Technology</h3>
At its core, an RFID system consists of three components: a tag, a reader, and a backend database. The tag, which includes a microchip and an antenna, stores unique identification data. When the reader emits a radio frequency signal, it powers the tag (in the case of passive tags) or activates it (for active tags), prompting the tag to transmit its stored data back to the reader. This data is then processed and matched with information in the database, enabling real-time tracking and authentication.
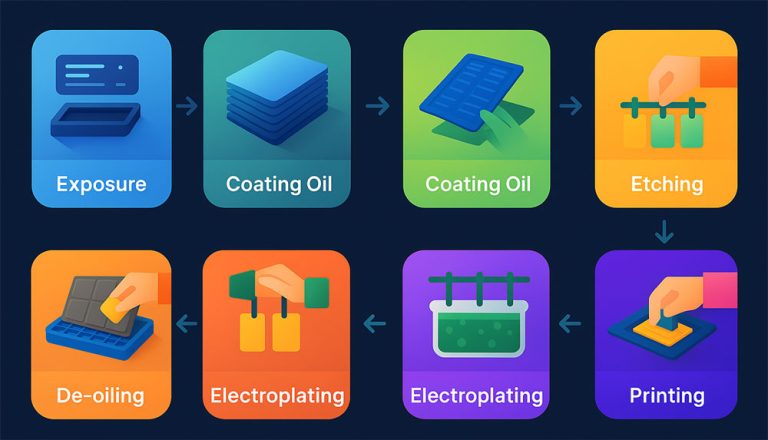
<h3>Incorporating Anti-Theft Features</h3>
The <strong>anti theft rfid tag</strong> builds upon this foundation by incorporating additional security layers. One common method is the use of Electronic Article Surveillance (EAS) technology integrated with RFID. These tags are designed to trigger an alarm if they pass through designated exit points without being deactivated or removed properly. For instance, in retail environments, tags are deactivated at the point of sale upon purchase. If an item with an active tag attempts to leave the store, readers at the exit detect it and sou
The Use of RFID for Human Identity Verification
Email: mtinfo007@gmail.com





